What is Vector Similarity? Understanding its Role in AI Applications.
Qdrant Team
·February 24, 2024

Understanding Vector Similarity: Powering Next-Gen AI Applications
A core function of a wide range of AI applications is to first understand the meaning behind a user query, and then provide relevant answers to the questions that the user is asking. With increasingly advanced interfaces and applications, this query can be in the form of language, or an image, an audio, video, or other forms of unstructured data.
On an ecommerce platform, a user can, for instance, try to find ‘clothing for a trek’, when they actually want results around ‘waterproof jackets’, or ‘winter socks’. Keyword, or full-text, or even synonym search would fail to provide any response to such a query. Similarly, on a music app, a user might be looking for songs that sound similar to an audio clip they have heard. Or, they might want to look up furniture that has a similar look as the one they saw on a trip.
How Does Vector Similarity Work?
So, how does an algorithm capture the essence of a user’s query, and then unearth results that are relevant?
At a high level, here’s how:
- Unstructured data is first converted into a numerical representation, known as vectors, using a deep-learning model. The goal here is to capture the ‘semantics’ or the key features of this data.
- The vectors are then stored in a vector database, along with references to their original data.
- When a user performs a query, the query is first converted into its vector representation using the same model. Then search is performed using a metric, to find other vectors which are closest to the query vector.
- The list of results returned corresponds to the vectors that were found to be the closest.
At the heart of all such searches lies the concept of vector similarity, which gives us the ability to measure how closely related two data points are, how similar or dissimilar they are, or find other related data points.
In this document, we will deep-dive into the essence of vector similarity, study how vector similarity search is used in the context of AI, look at some real-world use cases and show you how to leverage the power of vector similarity and vector similarity search for building AI applications.
Understanding Vectors, Vector Spaces and Vector Similarity
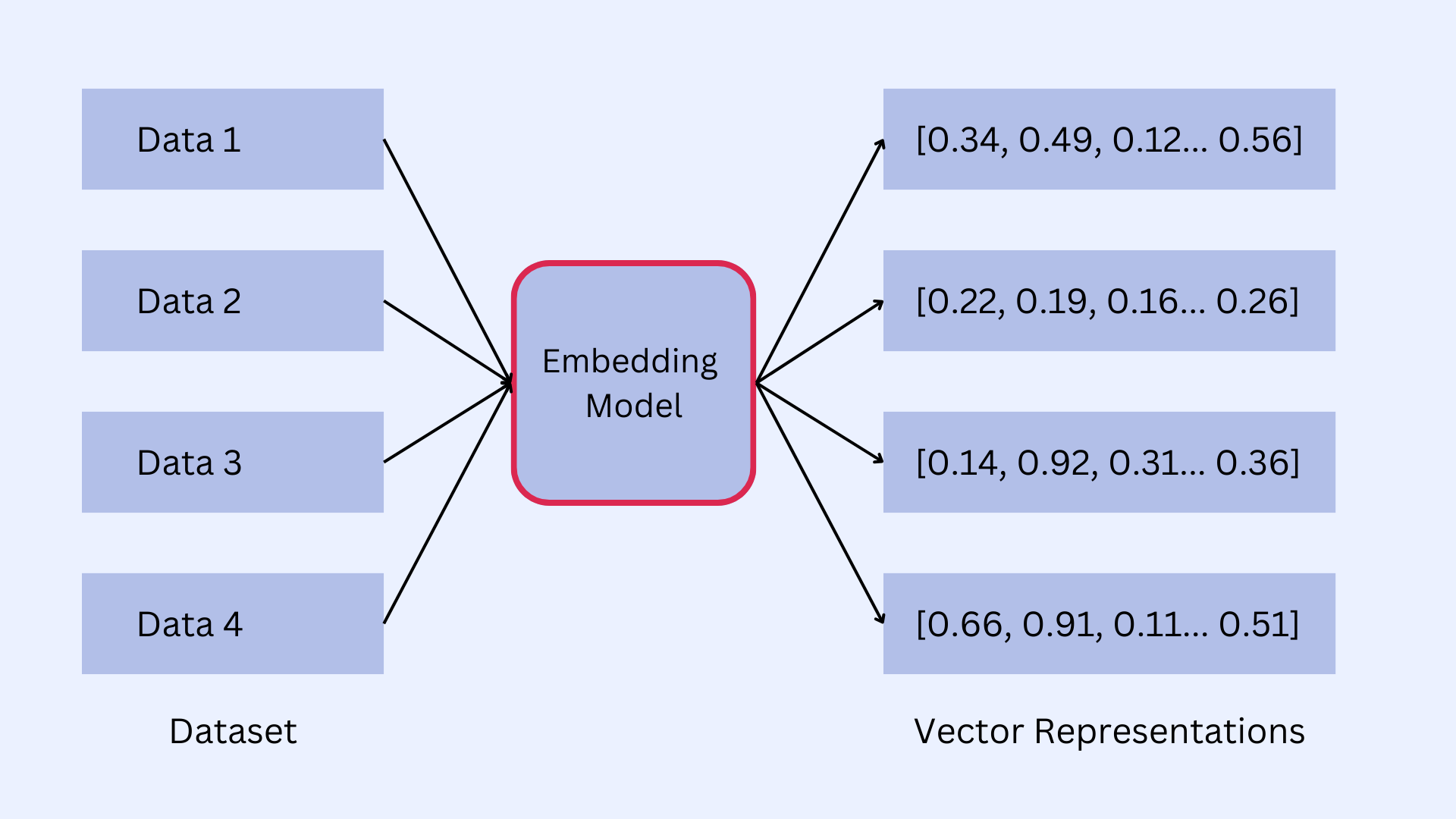
ML and deep learning models require numerical data as inputs to accomplish their tasks. Therefore, when working with non-numerical data, we first need to convert them into a numerical representation that captures the key features of that data. This is where vectors come in.
A vector is a set of numbers that represents data, which can be text, image, or audio, or any multidimensional data. Vectors reside in a high-dimensional space, the vector space, where each dimension captures a specific aspect or feature of the data.
Working
The number of dimensions of a vector can range from tens or hundreds to thousands, and each dimension is stored as the element of an array. Vectors are, therefore, an array of numbers of fixed length, and in their totality, they encode the key features of the data they represent.
Vector embeddings are created by AI models, a process known as vectorization. They are then stored in vector stores like Qdrant, which have the capability to rapidly search through vector space, and find similar or dissimilar vectors, cluster them, find related ones, or even the ones which are complete outliers.
For example, in the case of text data, “coat” and “jacket” have similar meaning, even though the words are completely different. Vector representations of these two words should be such that they lie close to each other in the vector space. The process of measuring their proximity in vector space is vector similarity.
Vector similarity, therefore, is a measure of how closely related two data points are in a vector space. It quantifies how alike or different two data points are based on their respective vector representations.
Suppose we have the words “king”, “queen” and “apple”. Given a model, words with similar meanings have vectors that are close to each other in the vector space. Vector representations of “king” and “queen” would be, therefore, closer together than “king” and “apple”, or “queen” and “apple” due to their semantic relationship. Vector similarity is how you calculate this.
An extremely powerful aspect of vectors is that they are not limited to representing just text, image or audio. In fact, vector representations can be created out of any kind of data. You can create vector representations of 3D models, for instance. Or for video clips, or molecular structures, or even protein sequences.
There are several methodologies through which vectorization is performed. In creating vector representations of text, for example, the process involves analyzing the text for its linguistic elements using a transformer model. These models essentially learn to capture the essence of the text by dissecting its language components.
How Is Vector Similarity Calculated?
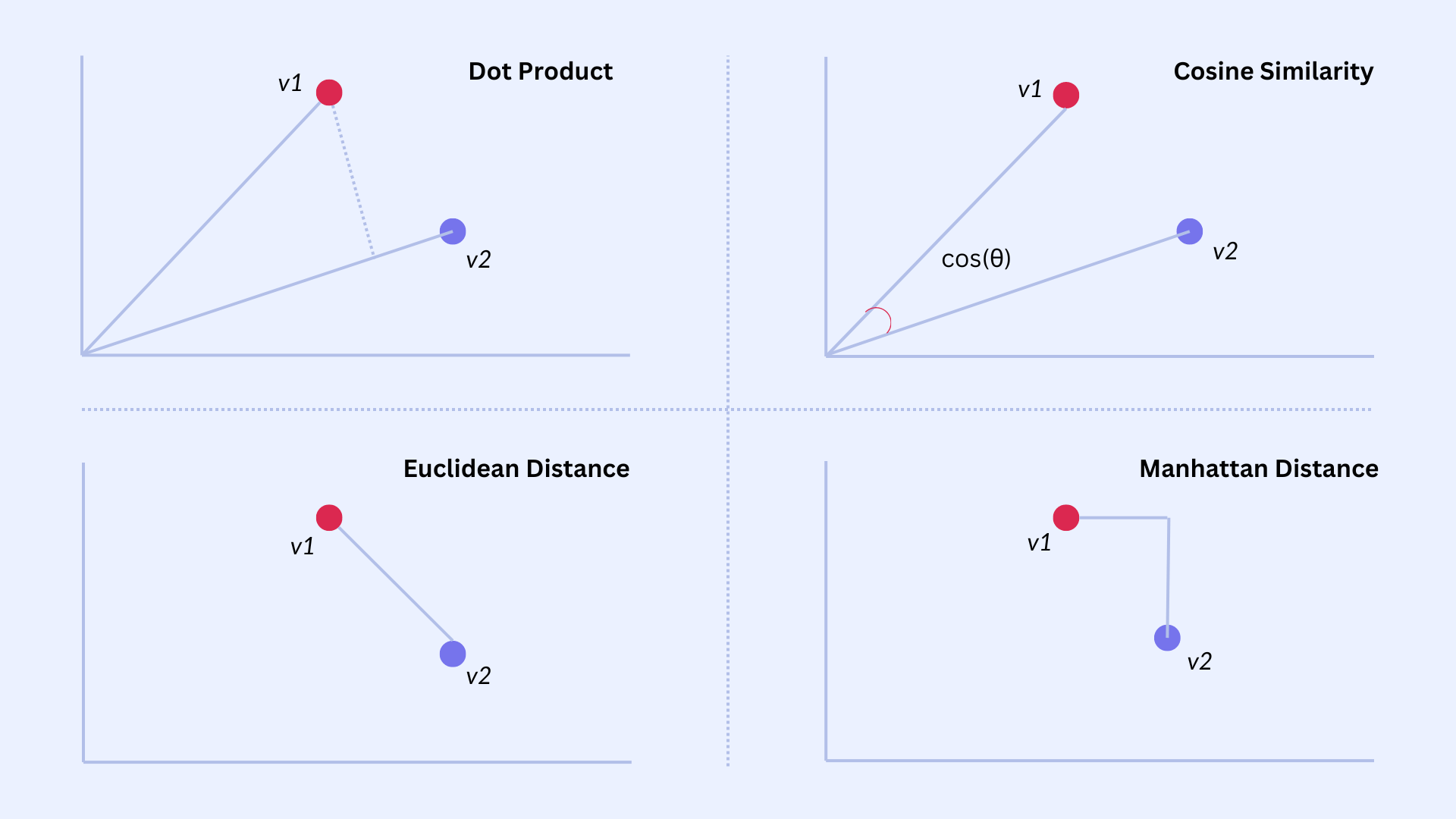
There are several ways to calculate the similarity (or distance) between two vectors, which we call metrics. The most popular ones are:
Dot Product: Obtained by multiplying corresponding elements of the vectors and then summing those products. A larger dot product indicates a greater degree of similarity.
Cosine Similarity: Calculated using the dot product of the two vectors divided by the product of their magnitudes (norms). Cosine similarity of 1 implies that the vectors are perfectly aligned, while a value of 0 indicates no similarity. A value of -1 means they are diametrically opposed (or dissimilar).
Euclidean Distance: Assuming two vectors act like arrows in vector space, Euclidean distance calculates the length of the straight line connecting the heads of these two arrows. The smaller the Euclidean distance, the greater the similarity.
Manhattan Distance: Also known as taxicab distance, it is calculated as the total distance between the two vectors in a vector space, if you follow a grid-like path. The smaller the Manhattan distance, the greater the similarity.
Metrics
As a rule of thumb, the choice of the best similarity metric depends on how the vectors were encoded.
Of the four metrics, Cosine Similarity is the most popular.
The Significance of Vector Similarity
Vector Similarity is vital in powering machine learning applications. By comparing the vector representation of a query to the vectors of all data points, vector similarity search algorithms can retrieve the most relevant vectors. This helps in building powerful similarity search and recommendation systems, and has numerous applications in image and text analysis, in natural language processing, and in other domains that deal with high-dimensional data.
Let’s look at some of the key ways in which vector similarity can be leveraged.
Image Analysis
Once images are converted to their vector representations, vector similarity can help create systems to identify, categorize, and compare them. This can enable powerful reverse image search, facial recognition systems, or can be used for object detection and classification.
Text Analysis
Vector similarity in text analysis helps in understanding and processing language data. Vectorized text can be used to build semantic search systems, or in document clustering, or plagiarism detection applications.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Vector similarity can help in representing and comparing linguistic features, from single words to entire documents. This can help build retrieval augmented generation (RAG) applications, where the data is retrieved based on user intent. It also enables nuanced language tasks such as sentiment analysis, synonym detection, language translation, and more.
Recommender Systems
By converting user preference vectors into item vectors from a dataset, vector similarity can help build semantic search and recommendation systems. This can be utilized in a range of domains such e-commerce or OTT services, where it can help in suggesting relevant products, movies or songs.
Due to its varied applications, vector similarity has become a critical component in AI tooling. However, implementing it at scale, and in production settings, poses some hard problems. Below we will discuss some of them and explore how Qdrant helps solve these challenges.
Challenges with Vector Similarity Search
The biggest challenge in this area comes from what researchers call the “curse of dimensionality.” Algorithms like k-d trees may work well for finding exact matches in low dimensions (in 2D or 3D space). However, when you jump to high-dimensional spaces (hundreds or thousands of dimensions, which is common with vector embeddings), these algorithms become impractical. Traditional search methods and OLTP or OLAP databases struggle to handle this curse of dimensionality efficiently.
This means that building production applications that leverage vector similarity involves navigating several challenges. Here are some of the key challenges to watch out for.
Scalability
Various vector search algorithms were originally developed to handle datasets small enough to be accommodated entirely within the memory of a single computer.
However, in real-world production settings, the datasets can encompass billions of high-dimensional vectors. As datasets grow, the storage and computational resources required to maintain and search through vector space increases dramatically.
For building scalable applications, leveraging vector databases that allow for a distributed architecture and have the capabilities of sharding, partitioning and load balancing is crucial.
Efficiency
As the number of dimensions in vectors increases, algorithms that work in lower dimensions become less effective in measuring true similarity. This makes finding nearest neighbors computationally expensive and inaccurate in high-dimensional space.
For efficient query processing, it is important to choose vector search systems which use indexing techniques that help speed up search through high-dimensional vector space, and reduce latency.
Security
For real-world applications, vector databases frequently house privacy-sensitive data. This can encompass Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in customer records, intellectual property (IP) like proprietary documents, or specialized datasets subject to stringent compliance regulations.
For data security, the vector search system should offer features that prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Also, it should empower organizations to retain data sovereignty, ensuring their data complies with their own regulations and legal requirements, independent of the platform or the cloud provider.
These are some of the many challenges that developers face when attempting to leverage vector similarity in production applications.
To address these challenges head-on, we have made several design choices at Qdrant which help power vector search use-cases that go beyond simple CRUD applications.
How Qdrant Solves Vector Similarity Search Challenges
Qdrant is a highly performant and scalable vector search system, developed ground up in Rust. Qdrant leverages Rust’s famed memory efficiency and performance. It supports horizontal scaling, sharding, and replicas, and includes security features like role-based authentication. Additionally, Qdrant can be deployed in various environments, including hybrid cloud setups.
Here’s how we have taken on some of the key challenges that vector search applications face in production.
Efficiency
Our choice of Rust significantly contributes to the efficiency of Qdrant’s vector similarity search capabilities. Rust’s emphasis on safety and performance, without the need for a garbage collector, helps with better handling of memory and resources. Rust is renowned for its performance and safety features, particularly in concurrent processing, and we leverage it heavily to handle high loads efficiently.
Also, a key feature of Qdrant is that we leverage both vector and traditional indexes (payload index). This means that vector index helps speed up vector search, while traditional indexes help filter the results.
The vector index in Qdrant employs the Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) algorithm for Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) searches, which is one of the fastest algorithms according to benchmarks.
Scalability
For massive datasets and demanding workloads, Qdrant supports distributed deployment from v0.8.0. In this mode, you can set up a Qdrant cluster and distribute data across multiple nodes, enabling you to maintain high performance and availability even under increased workloads. Clusters support sharding and replication, and harness the Raft consensus algorithm to manage node coordination.
Qdrant also supports vector quantization to reduce memory footprint and speed up vector similarity searches, making it very effective for large-scale applications where efficient resource management is critical.
There are three quantization strategies you can choose from - scalar quantization, binary quantization and product quantization - which will help you control the trade-off between storage efficiency, search accuracy and speed.
Security
Qdrant offers several security features to help protect data and access to the vector store:
- API Key Authentication: This helps secure API access to Qdrant Cloud with static or read-only API keys.
- JWT-Based Access Control: You can also enable more granular access control through JSON Web Tokens (JWT), and opt for restricted access to specific parts of the stored data while building Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
- TLS Encryption: Additionally, you can enable TLS Encryption on data transmission to ensure security of data in transit.
To help with data sovereignty, Qdrant can be run in a Hybrid Cloud setup. Hybrid Cloud allows for seamless deployment and management of the vector database across various environments, and integrates Kubernetes clusters into a unified managed service. You can manage these clusters via Qdrant Cloud’s UI while maintaining control over your infrastructure and resources.
Optimizing Similarity Search Performance
In order to achieve top performance in vector similarity searches, Qdrant employs a number of other tactics in addition to the features discussed above.FastEmbed: Qdrant supports FastEmbed, a lightweight Python library for generating fast and efficient text embeddings. FastEmbed uses quantized transformer models integrated with ONNX Runtime, and is significantly faster than traditional methods of embedding generation.
Support for Dense and Sparse Vectors: Qdrant supports both dense and sparse vector representations. While dense vectors are most common, you may encounter situations where the dataset contains a range of specialized domain-specific keywords. Sparse vectors shine in such scenarios. Sparse vectors are vector representations of data where most elements are zero.
Multitenancy: Qdrant supports multitenancy by allowing vectors to be partitioned by payload within a single collection. Using this you can isolate each user’s data, and avoid creating separate collections for each user. In order to ensure indexing performance, Qdrant also offers ways to bypass the construction of a global vector index, so that you can index vectors for each user independently.
IO Optimizations: If your data doesn’t fit into the memory, it may require storing on disk. To optimize disk IO performance, Qdrant offers io_uring based async uring storage backend on Linux-based systems. Benchmarks show that it drastically helps reduce operating system overhead from disk IO.
Data Integrity: To ensure data integrity, Qdrant handles data changes in two stages. First, changes are recorded in the Write-Ahead Log (WAL). Then, changes are applied to segments, which store both the latest and individual point versions. In case of abnormal shutdowns, data is restored from WAL.
Integrations: Qdrant has integrations with most popular frameworks, such as LangChain, LlamaIndex, Haystack, Apache Spark, FiftyOne, and more. Qdrant also has several trusted partners for Hybrid Cloud deployments, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, Red Hat OpenShift, Vultr, OVHcloud, Scaleway, and DigitalOcean.
We regularly run benchmarks comparing Qdrant against other vector databases like Elasticsearch, Milvus, and Weaviate. Our benchmarks show that Qdrant consistently achieves the highest requests-per-second (RPS) and lowest latencies across various scenarios, regardless of the precision threshold and metric used.
Real-World Use Cases
Vector similarity is increasingly being used in a wide range of real-world applications. In e-commerce, it powers recommendation systems by comparing user behavior vectors to product vectors. In social media, it can enhance content recommendations and user connections by analyzing user interaction vectors. In image-oriented applications, vector similarity search enables reverse image search, similar image clustering, and efficient content-based image retrieval. In healthcare, vector similarity helps in genetic research by comparing DNA sequence vectors to identify similarities and variations. The possibilities are endless.
A unique example of real-world application of vector similarity is how VISUA uses Qdrant. A leading computer vision platform, VISUA faced two key challenges. First, a rapid and accurate method to identify images and objects within them for reinforcement learning. Second, dealing with the scalability issues of their quality control processes due to the rapid growth in data volume. Their previous quality control, which relied on meta-information and manual reviews, was no longer scalable, which prompted the VISUA team to explore vector databases as a solution.
After exploring a number of vector databases, VISUA picked Qdrant as the solution of choice. Vector similarity search helped identify similarities and deduplicate large volumes of images, videos, and frames. This allowed VISUA to uniquely represent data and prioritize frames with anomalies for closer examination, which helped scale their quality assurance and reinforcement learning processes. Read our case study to learn more.
Future Directions and Innovations
As real-world deployments of vector similarity search technology grows, there are a number of promising directions where this technology is headed.
We are developing more efficient indexing and search algorithms to handle increasing data volumes and high-dimensional data more effectively. Simultaneously, in case of dynamic datasets, we are pushing to enhance our handling of real-time updates and low-latency search capabilities.
Qdrant is one of the most secure vector stores out there. However, we are working on bringing more privacy-preserving techniques in vector search implementations to protect sensitive data.
We have just about witnessed the tip of the iceberg in terms of what vector similarity can achieve. If you are working on an interesting use-case that uses vector similarity, we would like to hear from you.
Getting Started with Qdrant
Ready to implement vector similarity in your AI applications? Explore Qdrant’s vector database to enhance your data retrieval and AI capabilities. For additional resources and documentation, visit:
We are always available on our Discord channel to answer any questions you might have. You can also sign up for our newsletter to stay ahead of the curve.
























